Understanding The Dual Inline Package (DIP): A Comprehensive Guide
The dual inline package (DIP) has emerged as a pivotal component in the realm of electronics, particularly in the domain of circuit board design and integrated circuits. Its distinctive configuration allows for easy mounting on printed circuit boards (PCBs), making it a preferred choice for both hobbyists and professionals alike. In this article, we will delve deeper into what a dual inline package is, its advantages, and its applications in modern electronics. Understanding the intricacies of DIP will not only enhance your knowledge of electronic components but also equip you with the insights to make informed decisions in your projects.
The history of the dual inline package dates back to the 1960s, where it was primarily utilized for transistor-based circuits. Over the decades, it has evolved to accommodate various types of integrated circuits (ICs), leading to its widespread adoption across multiple industries. The significance of the DIP format lies in its ability to facilitate easy replacement and upgrades of components, thus extending the lifespan of electronic devices. As technology continues to advance, the relevance of DIP remains steadfast, serving as a reliable interface for connecting numerous electronic elements.
Moreover, the design of dual inline packages offers several advantages, including space efficiency, ease of soldering, and the ability to handle a higher pin count compared to other packaging types. These characteristics make DIP a popular choice for both low and high-volume production runs. In the following sections, we will explore various aspects of dual inline packages, including their construction, benefits, and common applications, providing you with a well-rounded understanding of this essential electronic component.
What is a Dual Inline Package (DIP)?
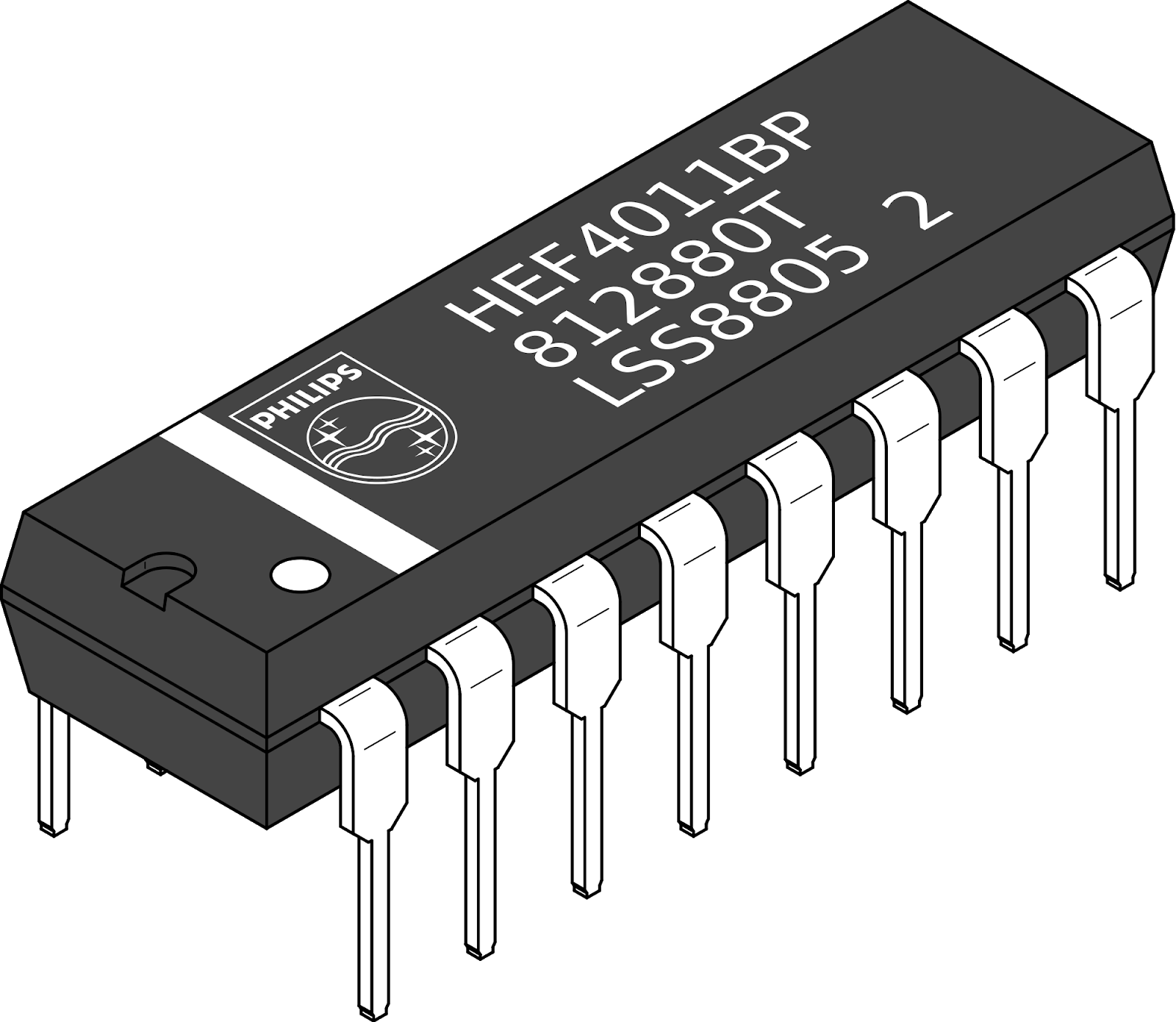
A dual inline package (DIP) is a type of electronic component packaging that features two parallel rows of pins. The pins are typically spaced at a standard distance, allowing for easy insertion into a PCB. DIPs come in various sizes, with the most common configurations being 8, 14, 16, 20, 24, and 28 pins. The design not only facilitates efficient signal routing but also allows for a compact layout, which is crucial in modern electronics.
What are the Advantages of Using Dual Inline Packages?
The dual inline package offers several advantages that make it an attractive choice for both manufacturers and hobbyists. Here are some key benefits:
- Ease of Use: DIPs are straightforward to handle, making them ideal for prototyping and testing.
- Cost-Effective: The manufacturing process for DIPs is relatively inexpensive, contributing to lower production costs.
- Space Efficiency: DIPs can accommodate a higher pin count while minimizing the overall footprint on the PCB.
- Reusability: Components in DIP format can be easily replaced, allowing for upgrades and repairs without needing to replace the entire circuit board.
Are There Different Types of Dual Inline Packages?
Yes, there are several types of dual inline packages, each designed for specific applications. Some common variations include:
- Standard DIP: The most common type, used for general applications.
- Wide DIP: Offers a wider spacing between pins for improved signal integrity.
- Stacked DIP: Features multiple layers stacked vertically for increased pin density.
- Low-Profile DIP: Designed for applications with height restrictions.
How is a Dual Inline Package Constructed?
The construction of a dual inline package typically involves a plastic or ceramic housing that encases the integrated circuit. The pins are usually made of metal and are soldered to the PCB through holes. The design ensures reliable electrical connections while protecting the internal components from environmental factors. The housing also plays a critical role in heat dissipation, which is essential for maintaining optimal performance.
What are the Applications of Dual Inline Packages?
Dual inline packages are used in a myriad of applications across different industries. Some of the most common applications include:
- Consumer Electronics: DIPs are prevalent in devices such as televisions, radios, and gaming consoles.
- Computers: Many computer peripherals and components, including memory chips, utilize DIP packaging.
- Automotive: DIPs are used in various automotive electronics for control systems and sensors.
- Industrial Equipment: Many industrial machines rely on DIPs for their electronic controls and monitoring systems.
How to Work with Dual Inline Packages?
Working with dual inline packages requires some basic tools and skills. Here’s a quick guide on how to get started:
- Tools Needed: You'll need a soldering iron, solder, and wire cutters.
- Preparation: Ensure your PCB is clean and the holes for the DIP are properly drilled.
- Soldering: Insert the DIP into the PCB, ensuring the pins align with the holes. Heat the soldering iron and apply solder to secure the connections.
- Testing: Once soldered, perform a continuity test to ensure all connections are secure.
What are the Future Prospects for Dual Inline Packages?
The future of dual inline packages looks promising as technology continues to evolve. While newer packaging formats like surface-mount technology (SMT) are gaining popularity, DIPs still hold a significant place in the market due to their ease of use and reliability. As demand for electronic components grows, especially in emerging technologies like IoT and AI, DIPs will likely continue to be utilized in various applications, particularly in prototyping and educational settings.
Conclusion: Why Choose Dual Inline Packages?
In summary, the dual inline package is a fundamental component in the electronic landscape, offering numerous advantages such as ease of use, cost-effectiveness, and versatility. Whether you're a hobbyist working on a DIY project or a professional involved in large-scale production, understanding the dual inline package will empower you to make informed choices about your electronic components. As technology progresses, the dual inline package will remain a reliable option for connecting and integrating various electronic devices, ensuring its relevance in the ever-evolving world of electronics.
In conclusion, the dual inline package (DIP) continues to be an essential element in circuit design, providing a blend of performance, reliability, and ease of use that is hard to match. By leveraging the advantages of DIPs and understanding their applications, you can enhance your projects and contribute to the advancements in electronics.
Article Recommendations
- How Old Is Brielle From Ellen
- Liza Weil
- Neil Young Images
- Cuanto Tiempo Gobernara Donal Trump
- Cnn What Does Donal Trump Want To Do With Violence
- Sean Mcdermott 9 11 Quote
- Which Shark Vacuum Is Better
- Gainbridge Fieldhouse Player Crossword
- What Is Tortured Poets
- How Did Rudolph The Red Nosed Reindeer Originated